
- 5 号 p. 419-
- 4 号 p. 268-
- 3 号 p. 136-
- 2 号 p. 67-
- 1 号 p. 1-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Kotaro Okada, Myu Hirota, Shungo Kumada, Yoshirnori Onuki2025 年 73 巻 5 号 p. 419-426
発行日: 2025/05/01
公開日: 2025/05/01
ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTML
電子付録Silica powder is an essential pharmaceutical ingredient, which in some combinations with drugs, causes chemical instability of the drug adsorbed on it. NMR measurements have been used to determine the drug adsorption state; however, the relationship between drug chemical stability and NMR relaxation, one of the NMR processes, is yet to be thoroughly studied. This work investigated the relationship between the chemical stability of itraconazole (ITZ)-adsorbed silica and its NMR relaxation. NMR can specifically observe 1H nuclei, and this feature was exploited to study only the T1 relaxation of these nuclei in the drug, excluding the silica signal composed of Si and O. ITZ, a poorly water-soluble model drug, was physically adsorbed on nonporous silica (Aerosil 200, AER), and mesoporous silica (Sylysia 320), and the 1H T1 relaxation was measured before storage using the time domain (TD)-NMR technique. The amount of ITZ degradant adsorbed in the silicas was also measured after storage at humidified conditions. Then, the relationship between the degradant amount of ITZ-adsorbed silica after storage and the T1 relaxation rate (1/T1) before storage was investigated. The ITZ-adsorbed silicas showed a positive correlation between the degradant amount and the 1/T1 value. ITZ-adsorbed AER showed a strong positive correlation (R2 = 0.751). Thus, the 1/T1 value may be an efficient parameter to determine the chemical stability of ITZ adsorbed on nonporous silica. The 1/T1 value measurement by TD-NMR could provide new insight for evaluating the chemical stability of solid dosage forms containing silica.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3635K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3635K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Fumihiko Ogata, Noriaki Nagai, Yugo Uematsu, Nanami Matsumoto, Chalerm ...2025 年 73 巻 5 号 p. 427-433
発行日: 2025/05/01
公開日: 2025/05/01
ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLThis study examined the potential of waste basil seeds (BSs) calcined at 500°C or 1000°C (BS500 or BS1000, respectively) for gadolinium removal from aqueous solutions. Gadolinium ion adsorption onto the produced adsorbents was also assessed in relation to a number of parameters, including initial concentration, adsorption temperature, exposure time, and pH. Higher initial concentrations, adsorption temperatures, and exposure times (BS, BS500 ≒ BS1000) resulted in an increase in the quantity of adsorbed gadolinium ions; To further understand the adsorption mechanism, detailed analyses of elemental distribution and binding energy were conducted. According to the proposed mechanism, gadolinium adsorption onto BS1000 may involve an ion exchange process, wherein hydrogen ions from functional groups such carboxyl and hydroxyl groups on the surface of BS1000 are replaced by gadolinium ions. Additionally, the effects of coexisting ions on gadolinium adsorption were investigated, revealing that while monovalent cations did not impact gadolinium ion adsorption capacity, divalent and trivalent cations significantly reduced it. Finally, the desorption of gadolinium ions was tested using desorption agents such as distilled water, hydrochloric acid, and sodium hydroxide. The results revealed that a 100 mmol/L hydrochloric acid solution was particularly effective for desorbing gadolinium ions. Overall, BS1000 demonstrates promising properties as an adsorbent for gadolinium ion removal from aqueous solutions.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1020K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1020K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Xiaohan Liu, Xinru Liu, Wenteng Zheng, Jing Xu, Tingting Chen, Tao Pen ...2025 年 73 巻 5 号 p. 434-444
発行日: 2025/05/08
公開日: 2025/05/08
ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTML
電子付録To search for safe and efficient anti-hypoxia active molecules, 27 derivatives were synthesized by introducing aminoalkyl groups at daidzein’s position-7 and position-8. The structures of these derivatives were confirmed by 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, and mass spectrometry. The anti-hypoxia activity was evaluated in vitro using a cell hypoxia model established with the AnaeroPack-anaero. The results showed that 9 compounds significantly enhanced cell viability under hypoxic conditions, with compounds 2a, 2b, 4d, 5a, and 5d exhibiting in vitro anti-hypoxia activity significantly superior to daidzein. And the drug-like properties prediction results of the target compounds indicated that compounds 2a, 2b, 4d, 5a, and 5d may also demonstrate favorable pharmacokinetic properties. Further, the anti-hypoxia activity in vivo of these 5 derivatives were evaluated via normobaric hypoxia and hypobaric hypoxia models. The results indicated that all of the 5 compounds extended the survival time of mice under normobaric hypoxia to varying degrees, and they also alleviated oxidative stress damage to the brain and heart of mice under hypobaric hypoxia. Among these, compound 2a demonstrated superior anti-hypoxia activity both in vitro and in vivo compared to daidzein, making it worthy of further study as a potential candidate for an anti-hypoxia drug.
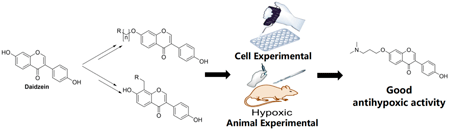 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3684K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3684K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Hiroaki Ikeda, Ami Mimura, Saki Makita, Kayo Funayama, Morihiro Shibas ...2025 年 73 巻 5 号 p. 445-448
発行日: 2025/05/08
公開日: 2025/05/08
ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTML
電子付録Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are a major cause of tumor recurrence; therefore, using CSC inhibitors is a potential strategy for cancer chemotherapy. We used our previously reported screening system that targets CSCs to identify a new scarce compound, streptospherin A (1), isolated from Streptomyces sp. KUSC-240. The planar structure of 1 was determined by high-resolution-MS (HR-MS) and NMR analysis. Nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy correlation and J-resolved heteronuclear multiple bond connectivity analysis revealed the partial relative configuration on the tetrahydropyran ring. Streptospherin A (1) inhibited CSC sphere formation and suppressed the growth of CSCs. These results suggest that streptospherin A (1) is a potential anticancer agent that may target CSCs.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1010K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1010K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Sana Ohashi, Sumie Ishiguro, Tsukasa Fukunaga, Akinobu Matsumoto, Mina ...2025 年 73 巻 5 号 p. 449-456
発行日: 2025/05/16
公開日: 2025/05/16
ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTML
電子付録The advent of mRNA medicine, initially implemented as a vaccine during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, has attracted interest in diverse therapeutic applications, including cancer vaccines and protein replacement therapies. Our group recently established a method for the complete chemical synthesis of mRNA. Although this approach has some advantages, chemically synthesized mRNA is limited to approximately 150 nucleotides in length and necessitates optimized designs for untranslated regions (UTRs) and coding sequences. To address this challenge, we investigated whether the non-reporter-based selection methods, including ribosome profiling and polysome profiling, which were often used for UTR optimization in long mRNA, could be adapted for short mRNA to identify highly translated UTR sequences. Using these methods, we collected mRNAs that interacted with ribosomes and analyzed their 5′-UTR sequences. We successfully identified a 9-nucleotide 5′-UTR that demonstrated approximately double the translation efficiency of the Kozak sequence, a widely used positive control. This work highlights the adaptability of ribosome-focused selection techniques for short, chemically synthesized mRNA and provides a foundation for effective sequence design. These findings advance the development of chemically synthesized mRNA as a viable alternative to in vitro-transcribed mRNA, paving the way for innovative therapeutic applications.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1806K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1806K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Hayate Takasaki, Kentaro Kitazaki, Yurie Hadano, Hirotaka Murase, Jeon ...2025 年 73 巻 5 号 p. 457-466
発行日: 2025/05/17
公開日: 2025/05/17
ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTML
電子付録New nucleoside derivatives containing the imidazole (Imd), pyridine or pyrimidine catalytic group were designed for site-specific acetylation of 2′-OH of the RNA ribose moiety. When the RNA substrate was acetylated in the presence of acetic anhydride under alkaline conditions, Probe (Imd) containing the imidazole catalytic group acetylated with a high selectivity to the 2′-OH of the uridine opposite the catalytic nucleotide. Probe (Py-4N) containing the pyridine group showed a higher catalytic activity under neutral conditions with a high selectivity for the 2′-OH group of the 5′ side of the uridine opposite the catalytic nucleotide in about 80% modification yield within 10 min. This study has shown that the oligodeoxynucleotide incorporating the new nucleotide derivative with the catalytic group can be a useful tool for site-selective acetylation of RNA 2′-OH.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4229K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (4229K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Shohei Nakamura, Maya Shimasaki-Suzuki, Momoka Hamaoka, Ayumi Sakurada ...2025 年 73 巻 5 号 p. 467-477
発行日: 2025/05/21
公開日: 2025/05/21
ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTMLMini-tablets (MTs) allow for dosage adjustments according to children’s weight and age. However, it is difficult to manufacture MTs with robust physical properties, and various formulation techniques are required. Adding cellulose nanofiber (CNF), a highly functional biomass material, to MTs improved the hardness and disintegration; however, the large variation in the weight and drug content of the resulting MTs remained a challenge. Therefore, this study analyzed the physical properties of CNF-containing MTs of different particle sizes and evaluated the effect of the particle size on MT manufacturing. CNF300, with an average particle size of approximately 300 µm, was pulverized to prepare CNF100, averaging 100 µm. The formulation included CNF (10, 30, and 50%), lactose hydrate, paracetamol, and magnesium stearate. The pharmaceutical powders mixed were loaded into a rotary tablet press equipped with a 3-mm multiple-tip tooling and compressed at 2, 5, and 8 kN forces. CNF100-containing MTs were manufactured via direct powder compression, and they showed lower variations in weight and drug content than those containing CNF300. The tensile strength of MTs containing CNF100 was smaller than that of those containing CNF300; however, a strength of ≥1 MPa (corresponding to ≥30 N hardness of a regular tablet) was obtained by setting the compression force to ≥5 kN. The MTs containing 30% CNF100 disintegrated in ≤30 s, regardless of the compression force. Thus, using smaller CNF particle sizes enabled the manufacturing of an orally disintegrating MT with adequate hardness and disintegration properties while also minimizing variations in MT weight and drug content.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5882K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (5882K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Aya Yoshimura, Ryusuke Nakada, Toshiyuki Wakimoto2025 年 73 巻 5 号 p. 478-483
発行日: 2025/05/22
公開日: 2025/05/22
ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTML
電子付録Four teleocidin analogs were isolated from Streptomyces eurocidicus, along with teleocidin B3. A combination of MS and NMR analyses elucidated their structures, revealing teleocidin A2 acetate and teleocidin B3 acetate as newly isolated metabolites. Teleocidins A2 and B3, known metabolites, exhibited weak antibacterial activities against Kocuria rhizophila and Bacillus subtilis. Notably, membrane vesicles of Burkholderia multivorans modulated the production levels of teleocidin analogs in S. eurocidicus, upregulating teleocidin biosynthesis but downregulating the subsequent acetylation step.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (803K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (803K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Takahito Kuribara, Honoka Yuba, Hina Saito, Akiko Takaya, Masami Ishib ...2025 年 73 巻 5 号 p. 484-487
発行日: 2025/05/24
公開日: 2025/05/24
ジャーナル オープンアクセス HTML
電子付録Coumarins are widely found in medicinal plants and exhibit diverse biological properties, including antibacterial activities. Herein, we report the total synthesis of 5-geranyloxy-7-hydroxycoumarin, 5-geranyloxy-7-methoxycoumarin, and Murrayacoumarin A. The asymmetric synthesis of (+)-Murrayacoumarin A was achieved via regioselective asymmetric dihydroxylation, allowing the determination of absolute configuration at the C7′-position. In addition, the antibacterial activities of the synthesized natural products and their derivatives were evaluated.
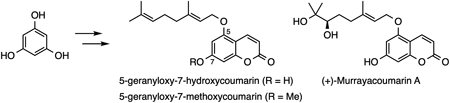 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (833K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (833K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|