
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Shinichi Sato2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 95-105
Shinichi Sato2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 95-105
発行日: 2022/02/01
公開日: 2022/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLProtein bioconjugation has become an increasingly important research method for introducing artificial functions in to protein with various applications, including therapeutics and biomaterials. Due to its amphiphilic nature, only a few tyrosine residues are exposed on the protein surface. Therefore, tyrosine residue has attracted attention as suitable targets for site-specific modification, and it is the most studied amino acid residue for modification reactions other than lysine and cysteine residues. In this review, we present the progress of our tyrosine chemical modification studies over the past decade. We have developed several different catalytic approaches to selectively modify tyrosine residues using peroxidase, laccase, hemin, and ruthenium photocatalysts. In addition to modifying tyrosine residues by generating radical species through single-electron transfer, we have developed a histidine modification method that utilizes singlet oxygen generated by photosensitizers. These highly reactive chemical species selectively modify proteins in close proximity to the enzyme/catalyst. Taking advantage of the spatially controllable reaction fields, we have developed novel methods for site-specific antibody modification, detecting hotspots of oxidative stress, and target identification of bioactive molecules.
 抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
抄録全体を表示Editor's pickIn this review, the author summarized his protein modification studies over the past decade. By utilizing highly reactive chemical species such as radical species and singlet oxygen, the author has developed novel methods for the selective modification of tyrosine and histidine residues, which have been difficult to be modified by conventional methods. In addition, The author took advantage of the high reactivity of these active species to apply protein modification reactions that proceed selectively in the space of a few nanometers around the catalyst.
PDF形式でダウンロード (2484K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Hirotaka Sasa, Koyo Mori, Kotaro Kikushima, Yasuyuki Kita, Toshifumi D ...2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 106-110
発行日: 2022/02/01
公開日: 2022/02/01
[早期公開] 公開日: 2021/12/11ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Benzolactams have unique biological activity and high utility in the synthesis of valuable compounds with direct applicability to oxindole alkaloids and antibacterial agents. Despite recent advances in organic chemistry and the growing number of reported methods for synthesizing benzolactams, their preparation still requires a multistep process. C–H amination reactions can convert aromatic C(sp2)–H bonds directly to C(sp2)–N bonds, and this direct approach to C–N bond formation offers effective access to benzolactams. Hypervalent iodine reagents are promising tools for achieving oxidative C–H amination. Motivated by our ongoing research efforts toward the development of useful hypervalent-iodine-mediated oxidative transformations, we herein describe an effective intramolecular oxidative C–H amination reaction based on μ-oxo hypervalent iodine catalysis for the synthesis of benzolactams bearing various functional groups.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (695K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (695K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Yoshio Nishimura, Hidetomo Kikuchi, Takanori Kubo, Rie Arai, Yuki Togu ...2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 111-119
発行日: 2022/02/01
公開日: 2022/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録An efficient synthetic method for novel 4,4-disubstituted 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones 5 and -thiones 6 was developed. The cyclocondensation reaction of O-methylisourea hemisulfate salt 11 with 8 gives a tautomeric mixture of dihydropyrimidines 12 and 13 following acidic hydrolysis of the cyclized products to produce 5 in high yields. Thionation reaction of 5 at the 2-position smoothly proceeds to give 2-thioxo derivatives 6. These compounds 5 and 6, corresponding to the products of a Biginelli-type reaction using urea or thiourea, a ketone and a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound, have long been inaccessible and hitherto unavailable for medicinal chemistry. These methods are invaluable for the synthesis of 5 and 6, which have been inaccessible by conventional methods. Therefore, the synthetic methods established in this study will expand the molecular diversity of their related derivatives. These compounds were also assessed for their antiproliferative effect on a human promyelocytic leukemia cell line, HL-60. Treatment of 10 µM 6b and 6d showed high inhibitory activity similarly to 1 µM all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), indicating that the 2-thioxo group and length of two alkyl substituents at the 4-position are strongly related to activity.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (838K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (838K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Takatoshi Kinoshita, Chihiro Tsunoda, Satoru Goto, Kanji Hasegawa, Hit ...2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 120-129
発行日: 2022/02/01
公開日: 2022/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Certain combinations of acidic and basic drugs can cause significant changes in physicochemical properties through the formation of ionic liquids, eutectic mixtures, or deep eutectic solvents. In particular, combining indomethacin and lidocaine is known to result in apparent increases in both the partition coefficients (hydrophobicity) and aqueous solubilities (hydrophilicity). The physicochemical interactions between drugs change the water solubility of the drugs and affect the bio-availability of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Therefore, we need to clarify the mechanism of changes of water solubility of drugs through the physicochemical interactions. In the present study, we identified a thermodynamic factor that regulates the dissolution of a basic drug, in the presence of various acidic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The results demonstrated that enthalpy–entropy compensation plays a key role in the dissolution of drug mixtures and that relevant thermodynamic conditions should be considered.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1398K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1398K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Yurina Aoyama, Akiko Toyotama, Tohru Okuzono, Naohide Hirashima, Hirok ...2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 130-137
Yurina Aoyama, Akiko Toyotama, Tohru Okuzono, Naohide Hirashima, Hirok ...2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 130-137
発行日: 2022/02/01
公開日: 2022/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録The free electrons inside precious metals such as Au vibrate when the surface of the metal is irradiated with an electromagnetic wave of an appropriate frequency. This oscillation is referred to as surface plasmon resonance (SPR), and the resonance frequency varies with permittivity of the medium around the metal. SPR sensors are widely applied in the fields of bioscience and pharmaceutical sciences, including biosensing for drug discovery, biomarker screening, virus detection, and testing for food safety. Here, we fabricated a metal–insulator–metal (MIM) SPR sensor by constructing two-dimensional (2D) regular array of Au colloidal particles (2D colloidal crystals) on an insulator layer over a thin Au film coated on a glass substrate surface. The 2D crystals were fabricated by electrostatically adsorbing negatively charged three-dimensional crystals onto a positively charged thin insulator formed on Au film. The plasmon peaks/dips from the MIM structure were measured in aqueous solutions of ethylene glycol (EG) at various concentrations. Multiple plasmon peaks/dips were observed due to the localized SPR (LSPR) of the Au particles and the Fano resonance between the Au particles and thin film. The plasmon peaks/dips shifted to higher wavelengths on increasing EG concentrations due to an increase in the refractive index of the media. The observed peak/dip shift was approximately twice that of LSPR from an isolated Au particle. We expect the present MIM substrate will be useful as a highly sensitive sensor in the pharmaceutical field.
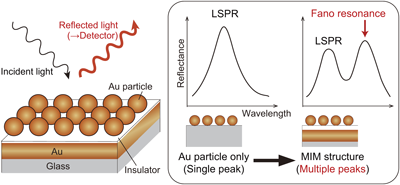 抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
抄録全体を表示Editor's pickSurface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensors have been widely applied in various fields of biotechnology and pharmacology, including drug discovery, biomarker screening, virus detection, and food safety testing. In this report, a metal-insulator-metal (MIM) type SPR sensor was fabricated by placing an insulator layer on top of a gold thin film and then arranging gold colloidal particles in a two-dimensional regular array on the insulator layer. Because of resonance of the plasmons of the gold particles and the thin film, multiple plasmon peaks/dips were observed. The substrate was shown to have twice the sensing capability of the gold particles.
PDF形式でダウンロード (3628K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Mariko Kimoto, Toshiyasu Sakane, Hidemasa Katsumi, Akira Yamamoto2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 138-145
発行日: 2022/02/01
公開日: 2022/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLThe dissolution behaviors of base excipients from sustained-release formulations have been investigated using various methodologies. However, the dissolution of polymers has not been fully evaluated because differences between formulations are still verified only by the release of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). In our previous study, we proposed a quick and simultaneous analysis of dissolved APIs and water-soluble polymers by ultra HPLC using charged aerosol and photodiode array detectors. The purpose of this study was to verify whether the analysis system could be adapted to other water-soluble polymers. Dissolution tests were conducted using matrix model tablets prepared from three polymers and three APIs (propranolol, ranitidine, and cilostazol) with different solubilities. The dissolution profiles of the polymers and APIs were determined using the proposed analysis system and compared. The results clarified differences in the dissolution behaviors of the APIs and polymers. The polymers, especially hydroxypropyl cellulose, exhibited the dissolution properties characteristic of each model formulation. Propranolol and ranitidine showed the diffusion type, while cilostazol showed the erosion type release mechanism due to their different solubilities. The release of cilostazol was delayed in all models compared to the polymer, which may be due to the aggregation of cilostazol in the gel layer. This analytical method can be used to study the dissolution behavior (diffusion or erosion) of APIs from matrix tablets containing various polymers. This method will provide useful information on release control, which will make it easier and more efficient to design appropriate formulations and analyze the release mechanisms.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3581K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (3581K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Yuta Takamura, Ken-ichi Morishita, Shota Kikuzawa, Masaki Watanabe, Hi ...2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 146-154
Yuta Takamura, Ken-ichi Morishita, Shota Kikuzawa, Masaki Watanabe, Hi ...2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 146-154
発行日: 2022/02/01
公開日: 2022/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Small-molecular drugs, which are generally inexpensive compared with biopharmaceuticals and can often be taken orally, may contribute to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) adopted by the United Nations. We previously reported the retinoid X receptor (RXR) agonist 4-(ethyl(3-isobutoxy-4-isopropylphenyl)amino)benzoic acid (NEt-3IB, 1) as a small-molecular drug candidate to replace biopharmaceuticals for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. The previous synthetic method to 1 required a large amount of organic solvent and extensive purification. In line with the SDGs, we aimed to develop an environmentally friendly, inexpensive method for the large-scale synthesis of 1. The developed method requires only a hydrophobic ether and EtOH as reaction and extraction solvents. The product was purified by recrystallization twice to afford 99% pure 1 at 100 mmol scale in about 30% yield. The optimized process showed a 35-fold improvement of the E-factor (an index of environmental impact) compared to the original method. This work, which changes the solvent used to environmentally preferable ones based on the existing synthetic method for 1, illustrates how synthetic methods for small-molecular drugs can be adapted and improved to contribute to the SDGs.
 抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
抄録全体を表示Editor's pickThe United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide guidelines for achieving a better and more sustainable future. Small-molecular drugs contribute to SDG3 (“Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages”), and waste reduction in small-molecular drug syntheses contributes to SDG6 (“Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all”) . The authors described an environmentally friendly scaled-up synthetic method for retinoid X receptor agonist NEt-3IB, a candidate for treating inflammatory bowel disease, by employing a reusable hydrophobic ether and ethanol.
PDF形式でダウンロード (1265K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Shinsuke Inuki, Hitomi Tabuchi, Chiaki Matsuzaki, Yasunori Yonejima, K ...2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 155-161
Shinsuke Inuki, Hitomi Tabuchi, Chiaki Matsuzaki, Yasunori Yonejima, K ...2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 155-161
発行日: 2022/02/01
公開日: 2022/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Exopolysaccharides (EPSs) occur widely in natural products made by bacteria, fungi and algae. Some EPSs have intriguing biological properties such as anticancer and immunomodulatory activities. Our group has recently found that EPSs generated from Leuconostoc mesenteroides ssp. mesenteroides strain NTM048 (NTM048 EPS) enhanced a production of mucosal immunoglobulin A (IgA) of mouse. Herein, we described the synthesis and evaluation of the tetrasaccharide fragments of NTM048 EPS to obtain information about the molecular mechanism responsible for the IgA-inducing activity.
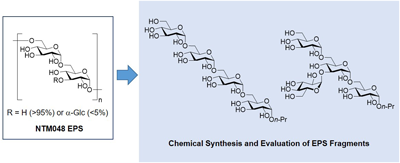 抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
抄録全体を表示Editor's pickExtracellular polysaccharides (EPSs) are carbohydrate polymers secreted by bacteria, fungi and algae, and have various biological activities. EPSs from Leuconostoc mesenteroides subsp. mesenteroides strain NTM048 (NTM048 EPS) enhance IgA production of mouse. In this study, the authors developed efficient synthetic routes to the NTM048 EPS fragments and evaluated their effects on IgA-inducing activity. The synthetic fragments showed a slight IgA-inducing activity, but the levels were not as high as those of the NTM048 EPS, revealing that the activity by EPS might be associated with the recognition of larger fragments or whole glucans, rather than the recognition of glycan substructures.
PDF形式でダウンロード (680K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Yuya Chiba, Kotaro Okada, Yoshihiro Hayashi, Kok Hoong Leong, Shungo K ...2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 162-168
発行日: 2022/02/01
公開日: 2022/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTMLNMR relaxometry measurement by time domain NMR (TD-NMR) is a promising technique for characterizing the properties of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). This study is dedicated to identifying the salt and free base of APIs by NMR relaxometry measured by the TD-NMR technique. Procaine (PC) and tetracaine (TC) were selected as model APIs to be tested. By using conventional methods including powder X-ray diffraction and differential scanning calorimetry, this study first confirmed that the salt and free base of the tested APIs differ from each other in their crystalline form. Subsequently, measurements of T1 and T2 relaxation were performed on the tested APIs using TD-NMR. The results demonstrated that these NMR relaxometry measurements have sufficient capacity to distinguish the difference between the free base and salt of the tested APIs. Furthermore, quantification of the composition of the binary powder blends consisting of salt and free bases was conducted by analyzing the acquired T1 and T2 relaxation curves. The analysis of the T1 relaxation curves provided a partly acceptable estimation: a good estimation of the composition was observed from PC powders, whereas for TC powders the estimation accuracy changed with the free base content in the binary blends. For the analysis on T2 relaxation curves, a precise estimation of the composition was observed from all the samples. From these findings, the NMR relaxometry measurement by TD-NMR, in particular the T2 relaxation measurement, is effective for evaluating the properties of APIs having different crystalline forms.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1050K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1050K) HTML形式で全画面表示
-
Shiori Takashina, Miki Takahashi, Koji Morimoto, Koichi Inoue2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 169-174
発行日: 2022/02/01
公開日: 2022/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Cannabidiol (CBD), a major non-psychoactive cannabinoid, has a lot of attention due to its potential relaxing properties and led the trend in commercial CBD aroma/oral hemp seed oil from the Japanese market. In this study, a routine assay for evaluating CBD oil samples was performed using LC coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and was used to apply the convertible tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in acetic acid conditions. Based on the electrospray positive ion mode, the detection of cannabidiolic acid (CBDA; m/z 359 > 219), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA; m/z 361 > 343), cannabigerol (CBG; m/z 317 > 193), CBD (m/z 315 > 193), THC (m/z 315 > 193) and cannabinol (CBN; m/z 311 > 223) was performed by satisfying separation with high density of C18 column. Oil samples (50 mg) were diluted with isopropanol (5 mL), to which stable isotope internal standards were added by dilution with methanol/water (50/50), and accuracy rates ranged from 97.8 to 102.2%. This method was used to evaluate the CBD oil products (5 kinds) from the Japanese market. Our survey found obvious counterfeit (non-detectable CBD) CBD oil from Japanese market. Following that, we investigated the conversion of THC in CBD oil samples in simple conditions such as 10% acetic acid and 70 °C for 6 h and discovered that converts THC proportions are approximately 5% ((THC content/CBD content) × 100) and <1.0%. Thus, our developed LC-MS/MS assay could be applied to monitor the CBD concentration and convertible THC from CBD oil.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (872K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (872K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Akihito Yokosuka, Tatsuya Shimomura, Shohei Yokogawa, Airi Oguro, Kats ...2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 175-181
発行日: 2022/02/01
公開日: 2022/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Two novel triterpene glycosides (1 and 2), 17 known triterpene glycosides (3–19), two known flavonoid glycosides (20 and 21), and two known norsesquiterpene glucosides (22 and 23) were isolated from Hedera rhombea (Araliaceae) leaves. The structures of 1 and 2 were determined by spectroscopic analysis, including two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy, and chromatographic analysis of the hydrolyzed products. The cytotoxicity of the isolated triterpene glycosides (1–19) against HL-60 human promyelocytic leukemia cells was evaluated. Compounds 9, 10, and 11 were cytotoxic to HL-60 cells with IC50 values of 7.2, 21.9, and 32.8 µM, respectively. Other compounds isolated from the leaves were not cytotoxic at sample concentrations of 50 μM.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (850K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (850K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
Hironori Suzuki, Asumi Tomita, Masataka Ito, Shuji Noguchi2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 182-186
発行日: 2022/02/01
公開日: 2022/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録Bromine K-edge X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy analyses were used to evaluate the crystals of the active pharmaceutical ingredients, eletriptan hydrobromide, dextromethorphan hydrobromide and scopolamine hydrobromide salts and the solid dispersion of eletriptan hydrobromide. The crystals and the solid dispersion of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) salts could be discriminated based on the shape of the XANES spectra. The differences in the shape of XANES spectra was ascribable to the differences in the interatomic interactions of the bromine ions based on the crystal structures. Ratio of the eletriptan hydrobromide α-form crystal in mixed powders of α-form and monohydrate crystals could be quantified by the linear-combination fitting using their XANES spectra. These results indicated that the XANES spectroscopy are a potent method for evaluating the APIs of pharmaceutical formulations even at the higher energy region around the bromine K-edge of 13470 eV.
 抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1081K) HTML形式で全画面表示
抄録全体を表示PDF形式でダウンロード (1081K) HTML形式で全画面表示 -
 Nanako Nakashima, Jukiya Sakamoto, Kenta Rakumitsu, Mariko Kitajima, L ...2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 187-191
Nanako Nakashima, Jukiya Sakamoto, Kenta Rakumitsu, Mariko Kitajima, L ...2022 年 70 巻 2 号 p. 187-191
発行日: 2022/02/01
公開日: 2022/02/01
ジャーナル フリー HTML
電子付録A new pentacyclic monoterpenoid indole alkaloid glycoside named secorubenine (1) was isolated from the heartwood of Adina rubescens, collected in Indonesia. The structure was elucidated by spectroscopic analysis and chemical modification of isolated secorubenine (1). The bioinspired enantioselective total synthesis of 1 was accomplished in 12 steps, whereafter its structure was determined and the absolute stereochemistry was confirmed.
 抄録全体を表示Editor's pick
抄録全体を表示Editor's pickThe authors have isolated a new pentacyclic monoterpenoid indole alkaloid glycoside, named secorubenine, from the heartwood of Adina rubescens, a plant used as a traditional medicine in Southeast Asia. Its structure was determined by careful analysis of the collected NMR spectra and chemical modification of the isolated natural product. Furthermore, the enantioselective total synthesis of secorbenine was immediately achieved by applying the bioinspired total synthesis of monoterpenoid indole alkaloid glycosides previously established by the authors. Thus, the exact structure of secorubenine, including absolute stereochemistry, was confirmed.
PDF形式でダウンロード (609K) HTML形式で全画面表示
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|